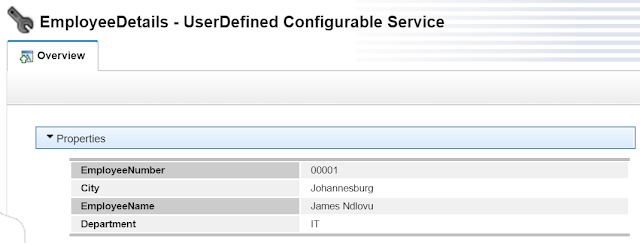
I created a UserDefined configurable service with the following values:
EmployeeDetails
EmployeeNumber: O0001
EmployeeName: James Ndlovu
Department: IT
City: Johannesburg
In the LocalEnvironment set the EmployeeNUmber in Variables/EmployeeNumber which I want to use to retrive the Employee Details from the config service.
To create the Java code, right-click the JavaCompute node and click Open Java to create and open a Java™ file in the Editor view.
Create the Java class for the node in which you want to include IBM Integration API methods.
Add the IBM Integration API JAR file install_dir/common/classes/IntegrationAPI.jar to the Java build path for the associated Java project.
Import com.ibm.broker.config.proxy.* in your code.
try {
// create new message as a copy of the input
MbMessage outMessage = new MbMessage(inMessage);
outAssembly = new MbMessageAssembly(inAssembly, outMessage);
/*get employee details from local environment variable */ MbMessage localEnv = inAssembly.getLocalEnvironment(); MbElement empNoVar = localEnv.getRootElement().getFirstElementByPath("Variables/EmployeeNumber"); String employeeNumber = empNoVar.getValueAsString(); BrokerProxy b = BrokerProxy.getLocalInstance(); /*return an instance of the BrokerProxy object for the integration node to which the message flow (that contains this node) is deployed */ while (!b.hasBeenPopulatedByBroker()) { Thread.sleep(100); /*This ensures that the BrokerProxy object is populated with data from the integration node before you access the configurable service */ } ConfigurableService vendorUDCS = b.getConfigurableService("UserDefined", "EmployeeDetails"); String employeeDetails = vendorUDCS.getProperties().getProperty(employeeNumber);
/*output the employeeDetails to a local environment variable*/ MbMessage newEnv = new MbMessage(localEnv);
newEnv.getRootElement().createElementAsFirstChild(MbElement.TYPE_NAME_VALUE, "EmpDetails", employeeDetails); outAssembly = new MbMessageAssembly(inAssembly, newEnv, inAssembly.getExceptionList(), inAssembly.getMessage()); b.disconnect();} catch (MbException e) {
// Re-throw to allow Broker handling of MbException
throw e;
}